Analysis of business intelligence analysis job market on Indeed (England & Switzerland)
(NOTES TO SELF:) INCLUDE AIMS & OBJECTIVES, DATA USED, APPROACH USED, CHALLENGES FACED (and HOW THESE WERE OVERCOME) (relevant codes, methodology, formulas etc.) Ideally include some custom SQL queries
Steps involved:
- Webscraping (Selenium)
- Data Analysis (NumPy, Pandas)
- Data Visualisation (Seaborn, Matplotlib, Power BI)
Libraries: Webscraping: Selenium Analysis: NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, Visualization (Seaborn, Matplotlib)
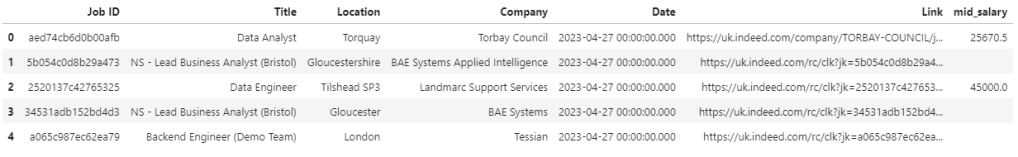
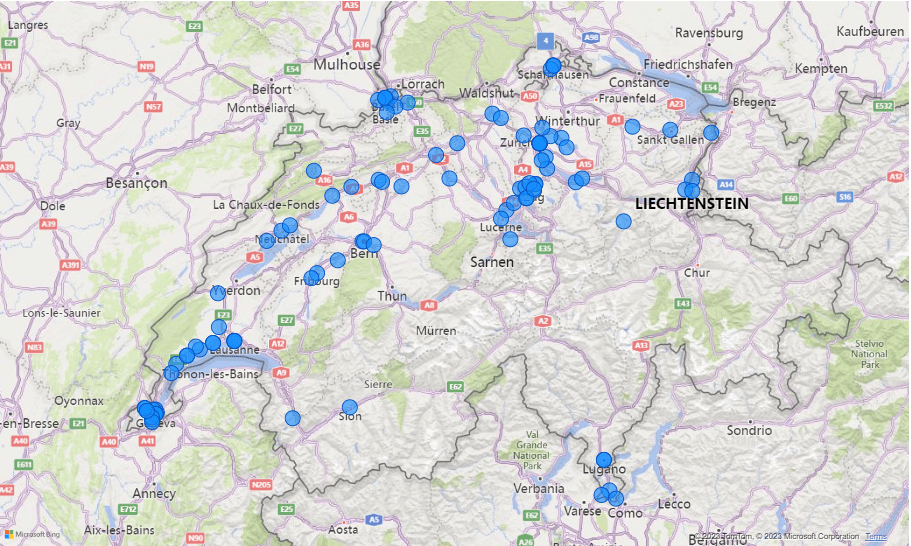
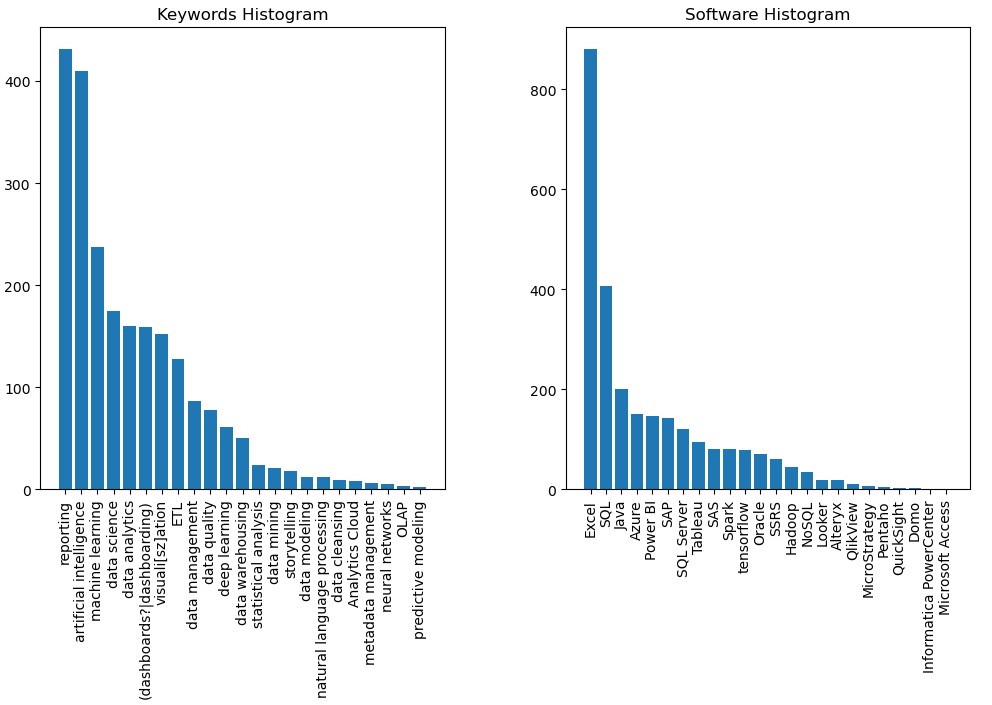
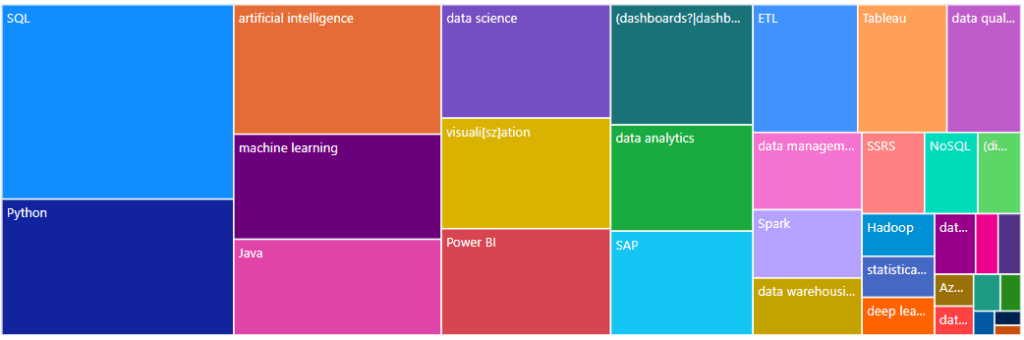
Output:
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import Select
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import datetime
import re
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
processed_job_ids = []
data = []
def calculate_posted_date(date_str):
if "Just posted" in date_str or "Today" in date_str:
return datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
elif "day" in date_str:
days_ago = int(re.search(r'\d+', date_str).group())
return (datetime.datetime.now() - datetime.timedelta(days=days_ago)).strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
elif "days ago" in date_str:
days_ago = int(re.search(r'\d+', date_str).group())
return (datetime.datetime.now() - datetime.timedelta(days=days_ago)).strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
else:
return '1900-01-01'
for country in ['uk', 'ch']:
for i in range(0, 500, 10):
if country == 'uk':
url = f'https://uk.indeed.com/jobs?q=Business+intelligence&l=England&sort=date&start={i}'
elif country == 'ch':
url = f'https://ch.indeed.com/Stellen?q=business+intelligence&sort=date&lang=en&vjk=f30739b891280aba&start={i}'
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.get(url)
job_listings = driver.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, 'job_seen_beacon')
for job in job_listings:
Job_ID = job.find_element(By.XPATH, './/a').get_attribute('data-jk')
Title = job.find_element(By.XPATH,'.//span[starts-with(@title, "")]').text
Location = job.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, "companyLocation").text
Company = job.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, "companyName").text
Date_str = job.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, "date").text
Date = calculate_posted_date(Date_str)
Country = country
try:
Link = job.find_element(By.XPATH,'.//a[starts-with(@id, "job_") and contains(@class, "jcs-JobTitle")]').get_attribute('href')
except:
Link = ""
try:
Salary = job.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, "attribute_snippet").text
except:
Salary = ""
driver.execute_script("window.open('');")
driver.switch_to.window(driver.window_handles[1])
if Link:
driver.get(Link)
try:
job_description = driver.find_element(By.ID, "jobDescriptionText").text
except:
job_description = ""
data.append([Country, Job_ID, Title, Location, Company, Date_str, Date, Link, Salary, job_description])
driver.close()
driver.switch_to.window(driver.window_handles[0])
driver.quit()
df = pd.DataFrame(data=data, columns=['Country', 'Job ID', 'Title', 'Location', 'Company', 'Date_str', 'Date', 'Link', 'Salary', 'Description'])
#Location cleanser
def extract_location(location):
location = str(location) # convert to string if not already
remote = ''
other_locations = ''
# check for hybrid remote in
if 'Hybrid remote in' in location:
remote = 'Hybrid remote'
location = re.sub('Hybrid remote in', '', location)
# check for remote in
if 'Remote in' in location:
remote = 'Remote'
location = re.sub('Remote in', '', location)
# check for +n locations or +n location
match = re.search('\+(\d+) location[s]?', location)
if match:
other_locations = match.group(1)
location = re.sub('\+\d+ location[s]?', '', location)
else:
other_locations = None
# return location, remote, and other locations as a tuple
return (location.strip(), remote.strip(), other_locations.strip() if other_locations is not None else None)
# apply the extract_location function to the Location column of df and store results in new columns
df[['Location', 'Remote', 'Other locations']] = df['Location'].apply(lambda x: pd.Series(extract_location(x)))
#SALARY CLEANSER
import re
import pandas as pd
# makes sure Salary is a string value
df['Salary_str'] = df['Salary'].astype(str)
# define a function to extract lower salary, upper salary and time unit from a string
def extract_salary_info(Salary_str):
# if salary is blank, return blank values
if Salary_str == "":
return "", "", ""
# use regex to find the salary range and time unit
pattern = r"£(\d+,\d+) - £(\d+,\d+) (a \w+)|£(\d+,\d+) (a \w+)|£(\d+) (a \w+)|£(\d+) - £(\d+) (a \w+)"
match = re.search(pattern, Salary_str)
# if match is found, extract the groups
if match:
lower_salary = match.group(1) or match.group(4) or match.group(6) or match.group(8) # use group 1 or 4 or 6 or 8 for lower salary
upper_salary = match.group(2) or match.group(4) or match.group(6) or match.group(9) # use group 2 or 4 or 6 or 9 for upper salary
time_unit = match.group(3) or match.group(5) or match.group(7) or match.group(10) # use group 3 or 5 or 7 or 10 for time unit
# remove commas from lower and upper salary
lower_salary = lower_salary.replace(",", "")
upper_salary = upper_salary.replace(",", "")
# return the extracted values
return lower_salary, upper_salary, time_unit
# if no match is found, return blank values
else:
return "", "", ""
# apply the function to the salary column and create new columns
df[["lower_salary", "upper_salary", "time_unit"]] = df["Salary_str"].apply(extract_salary_info).apply(pd.Series)
df['mid_salary'] = df.apply(lambda x: (float(x['lower_salary']) + float(x['upper_salary'])) / 2 if x['lower_salary'] and x['upper_salary'] else "", axis=1)
df['Working hours'] = np.where(df['Salary_str'].str.contains("Part-time"), "Part-time", "Full-time")
#EXTRACT KEYWORDS
#replaces blank description values
df['Description'].fillna('', inplace=True)
# define keywords
#Keywords = ['SAP', 'Analytics Cloud', 'Excel', 'Azure Synapse', 'Power BI', 'Tableau', 'SQL', '\bR\b', 'Python', 'Java', 'data mining', 'ETL', 'data warehousing', 'data modeling', 'visuali[sz]ation','business intelligence', '(dashboards?|dashboarding)', 'reporting', 'OLAP', 'data analytics', 'data science', 'machine learning', 'deep learning', 'neural networks', 'natural language processing', 'Tensor flow', 'artificial intelligence', 'predictive modeling', 'statistical analysis', 'data cleansing', 'data quality', 'metadata management', 'data management', 'Hadoop', 'Spark', 'NoSQL', 'SSRS']
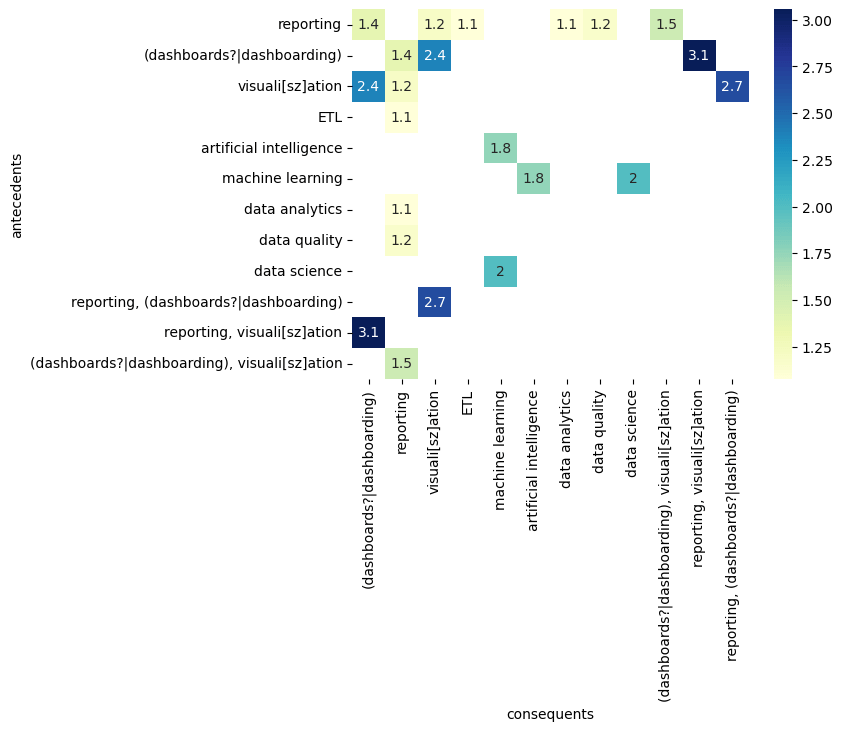
Keywords = ['Analytics Cloud', 'data mining', 'ETL', 'data warehousing', 'data modeling', 'visuali[sz]ation', '(dashboards?|dashboarding)', 'reporting', 'OLAP', 'storytelling', 'data analytics', 'data science', 'machine learning', 'deep learning', 'neural networks', 'natural language processing', 'Tensor flow', 'artificial intelligence', 'predictive modeling', 'statistical analysis', 'data cleansing', 'data quality', 'metadata management', 'data management']
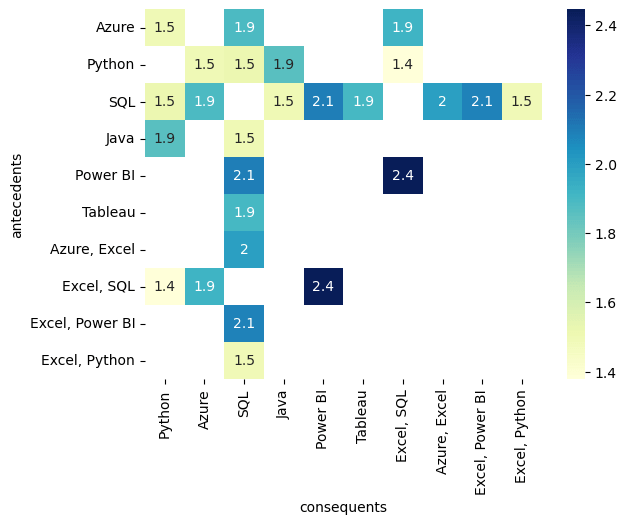
Software = ['Power BI', 'Tableau', 'Azure', 'Access', 'SQL Server', 'SQL', 'MySQL' 'Python', '\bR\b', 'Java', 'QlikView', 'SAP', 'IBM Cognos Analytics', 'SAS', 'MicroStrategy', 'Oracle', 'QuickSight', 'Alteryx', 'Domo', 'Looker', 'TIBCO Spotfire', 'tensorflow', 'Yellowfin BI', 'Pentaho', 'Informatica PowerCenter', 'Sisense', 'Excel', 'Hadoop', 'Spark', 'NoSQL', 'SSRS']
# create an empty dataframe to store the matched keywords
df_keywords = pd.DataFrame(columns=['K_Job_ID', 'Keywords'])
df_software = pd.DataFrame(columns=['K_Job_ID', 'Software'])
# loop through each row of the df dataframe
for idx, row in df.iterrows():
K_Job_ID = row['Job ID']
job_description = row['Description']
matched_keywords = []
matched_software = []
# loop through each keyword and check if it is in the job description
for keyword in Keywords:
if re.search(keyword, job_description, re.IGNORECASE):
matched_keywords.append(keyword)
# if any keywords are found, append them to the df_keywords dataframe
if matched_keywords:
for keyword in matched_keywords:
df_keywords = pd.concat([df_keywords, pd.DataFrame({'K_Job_ID': [K_Job_ID], 'Keywords': [keyword]})], ignore_index=True)
# loop through each keyword and check if it is in the job description
for software in Software:
if re.search(software, job_description, re.IGNORECASE):
matched_software.append(software)
# if any keywords are found, append them to the df_keywords dataframe
if matched_software:
for software in matched_software:
df_software = pd.concat([df_software, pd.DataFrame({'K_Job_ID': [K_Job_ID], 'Software': [software]})], ignore_index=True)